Analyzing the relationship between Bangladesh and Myanmar requires an exploration of historical, political, economic, and social factors that have shaped their interactions over time. In approximately 4000 words, I will delve into the complexities of their relationship, spanning from pre-colonial times to the contemporary challenges and opportunities they face. Let’s embark on this journey through the intricate tapestry of Bangladeshi-Myanmar relations.
Introduction
Bangladesh and Myanmar, two neighboring countries in South Asia, share a multifaceted relationship marked by historical ties, cultural exchanges, economic interactions, and geopolitical dynamics. Situated in a region of significant strategic importance, the relationship between these two nations has been influenced by colonial legacies, border disputes, refugee crises, economic interests, and diplomatic engagements. Understanding the nuances of their relationship requires an exploration of various dimensions, including historical contexts, political dynamics, economic cooperation, security concerns, and societal interactions. In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve into the historical evolution, contemporary challenges, and prospects of Bangladesh-Myanmar relations.
Historical Background
The historical interaction between Bangladesh (formerly East Pakistan) and Myanmar (formerly Burma) dates back centuries, characterized by trade relations, cultural exchanges, and occasional conflicts. The region encompassing present-day Bangladesh and Myanmar has witnessed the rise and fall of ancient civilizations, the spread of Buddhism, the influence of Indian and Southeast Asian empires, and the advent of colonial powers.
- Pre-Colonial Era: Both Bangladesh and Myanmar have rich historical legacies predating the colonial period. The Bengal region, including present-day Bangladesh, was renowned for its prosperous trade networks, vibrant culture, and intellectual contributions. Meanwhile, Myanmar was home to several powerful kingdoms, including the Pyu, Mon, and later, the Bamar (Burman) empire.
- Colonial Rule: The British Empire’s colonization of South Asia and Southeast Asia profoundly impacted the territories that now constitute Bangladesh and Myanmar. Burma became a province of British India in the 19th century, while Bengal was also under British rule. The partition of Bengal in 1947 led to the creation of East Pakistan, which later gained independence as Bangladesh in 1971.
- Post-Independence Period: Bangladesh’s emergence as an independent nation in 1971 following a bloody liberation war against Pakistan marked a significant turning point in the region’s history. Myanmar, too, gained independence from British rule in 1948, albeit under different circumstances. However, the legacy of colonialism left lasting imprints on both countries, shaping their socio-economic structures, political systems, and national identities.
Political Relations
The political relationship between Bangladesh and Myanmar has been influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including border disputes, ethnic tensions, refugee crises, diplomatic engagements, and regional dynamics. Despite occasional efforts to foster cooperation, the relationship has been characterized by periods of tension and mistrust.

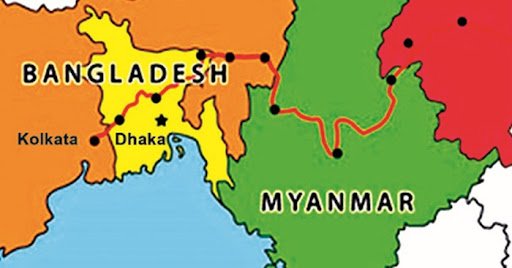
- Border Disputes: The unresolved border issues, particularly concerning the demarcation of the maritime boundary in the Bay of Bengal and the delineation of land borders, have been a source of contention between Bangladesh and Myanmar. Disputes over territorial sovereignty, maritime resources, and fishing rights have occasionally escalated tensions and hindered bilateral cooperation.
- Rohingya Crisis: One of the most pressing challenges in Bangladesh-Myanmar relations has been the Rohingya refugee crisis. The Rohingya, a Muslim minority group in Myanmar, have faced persecution and violence, leading to mass displacement and refugee flows into neighboring countries, particularly Bangladesh. The exodus of Rohingya refugees, especially since the 2017 military crackdown in Rakhine State, has strained bilateral relations and raised international concerns about human rights violations and humanitarian assistance.
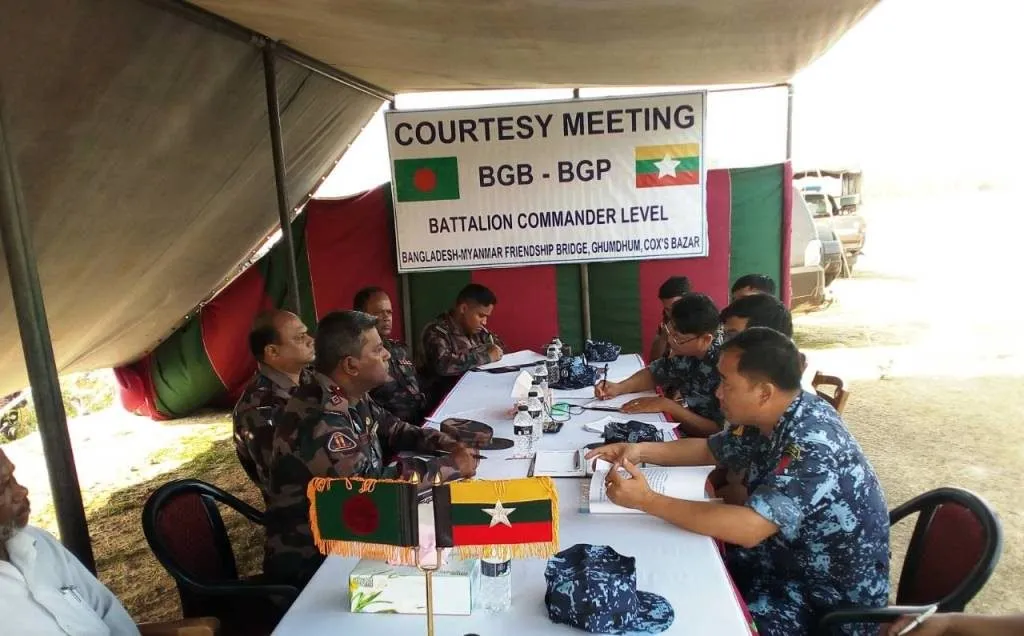
- Diplomatic Engagements: Despite the challenges, both Bangladesh and Myanmar have engaged in diplomatic dialogue to address bilateral issues and enhance cooperation in various domains. High-level visits, diplomatic negotiations, and multilateral forums have provided platforms for dialogue and conflict resolution. However, the efficacy of such diplomatic efforts in addressing fundamental issues remains a subject of debate.
- Regional Dynamics: The geopolitical landscape of South Asia and Southeast Asia, including the influence of neighboring powers such as China and India, has also shaped Bangladesh-Myanmar relations. Geostrategic considerations, economic interests, and security concerns have influenced the foreign policies of both countries, sometimes leading to alignments or divergences in their positions on regional issues.
Economic Cooperation
Economic ties between Bangladesh and Myanmar have evolved, encompassing trade relations, investment flows, energy cooperation, and infrastructure development. Despite the potential for economic collaboration, various challenges, including infrastructural constraints, regulatory barriers, and political uncertainties, have hindered the realization of their economic partnership’s full potential.
- Trade Relations: Bangladesh and Myanmar have engaged in bilateral trade, primarily in goods such as agricultural products, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods. However, trade volumes remain relatively modest compared to the potential due to logistical challenges, tariff barriers, and non-tariff barriers.
- Investment Flows: Both countries have sought to attract foreign investment to spur economic growth and development. However, factors such as regulatory frameworks, infrastructure deficits, bureaucratic hurdles, and political instability have limited the inflow of foreign investment. Efforts to promote investment cooperation through bilateral agreements and economic forums have been hampered by these challenges.
- Energy Cooperation: Energy cooperation holds promise for enhancing bilateral relations between Bangladesh and Myanmar. The discovery of natural gas reserves in Myanmar’s offshore fields has prompted exploration and production activities involving international energy companies. Bangladesh has expressed interest in importing natural gas from Myanmar to meet its growing energy demand, although logistical and commercial considerations have complicated such ventures.
- Infrastructure Development: Infrastructure development projects, including road connectivity, port facilities, and cross-border transportation networks, have been proposed to enhance connectivity and facilitate trade between Bangladesh and Myanmar. Initiatives such as the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project aim to improve transportation links between the two countries, albeit progress has been slow due to funding constraints and logistical challenges.
Security Concerns
Security considerations play a crucial role in shaping Bangladesh-Myanmar relations, encompassing border security, counterterrorism cooperation, maritime security, and regional stability. Both countries face common security challenges, including transnational crime, terrorism, and illicit trafficking, necessitating collaborative efforts to address shared threats.
- Border Security: Securing the porous border between Bangladesh and Myanmar remains a priority for both countries to prevent illegal crossings, smuggling, and other illicit activities. Border management initiatives, including joint patrols, intelligence sharing, and infrastructure development, have been pursued to enhance border security and control.
- Counterterrorism Cooperation: Bangladesh and Myanmar have cooperated in counterterrorism efforts to combat extremist groups and prevent cross-border terrorist activities. Intelligence sharing, joint operations, and capacity-building initiatives have been undertaken to strengthen counterterrorism cooperation and address emerging security threats.
- Maritime Security: Ensuring maritime security in the Bay of Bengal is essential for both Bangladesh and Myanmar, given the strategic significance of maritime trade routes, natural resource exploration, and maritime connectivity. Cooperation on maritime surveillance, search and rescue operations, and maritime domain awareness has been pursued to enhance maritime security and safety.
- Regional Stability: Bangladesh and Myanmar are key stakeholders in regional stability initiatives, including the Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC) and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). Engaging in regional forums and multilateral mechanisms allows both countries to address common challenges,
