India and Myanmar share a complex and multifaceted relationship, deeply rooted in historical, cultural, economic, and strategic ties. The bilateral relationship between these two countries has evolved over the years, shaped by various geopolitical factors and regional dynamics. In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll delve into the historical context, key areas of cooperation, challenges, and prospects of the India-Myanmar relationship.
Historical Background:
The history of India-Myanmar relations dates back Centuries, characterized by cultural exchanges, trade routes, and occasional conflicts. Myanmar, formerly known as Burma, shares a long border with India, fostering interactions between the two civilizations for centuries. Historical ties are evident through the influence of Indian culture, religion, and trade in Myanmar, particularly in regions like Manipur, Mizoram, and Nagaland.
During the colonial era, India and Myanmar were under British rule, significantly influencing their political landscapes. Post-independence, India, and Myanmar emerged as sovereign nations, striving to establish their identities and pursue development agendas.
Diplomatic Relations:
Diplomatic relations between India and Myanmar were established shortly after their independence. India was one of the first countries to recognize Myanmar’s sovereignty in 1948. Over the years, the two nations have maintained diplomatic ties, collaborating on various regional and international platforms such as the United Nations, ASEAN, and BIMSTEC.

Strategic Importance:
Myanmar holds strategic significance for India due to its geographical location, serving as a bridge between South Asia and Southeast Asia. The northeastern states of India share borders with Myanmar, making it crucial for India’s security and connectivity objectives. Additionally, Myanmar’s proximity to the Bay of Bengal and the Indian Ocean enhances its strategic relevance in the context of maritime security and trade routes.
Economic Cooperation:
Economic cooperation between India and Myanmar has expanded significantly in recent years. Trade relations encompass a wide range of sectors, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, energy, and infrastructure development. India is one of Myanmar’s major trading partners, with bilateral trade reaching billions of dollars annually.
Several infrastructure projects, such as the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway and the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project, aim to enhance connectivity between the two countries and facilitate trade. Furthermore, initiatives like the India-Myanmar Border Trade Agreement have streamlined cross-border trade, benefiting local communities on both sides.
Cultural and People-to-People Ties:
Cultural exchanges and people-to-people contacts play a crucial role in fostering goodwill and understanding between India and Myanmar. Both countries share historical and cultural affinities, reflected in traditions, festivals, and religious practices. Buddhism, which originated in India, has deep roots in Myanmar, serving as a cultural link between the two nations.
Tourism between India and Myanmar has also witnessed steady growth, with travelers exploring each other’s heritage sites, natural landscapes, and cultural attractions. Educational exchanges and scholarships further strengthen ties between Indian and Myanmarese students and academic institutions.
Security Cooperation:
Security cooperation between India and Myanmar is vital for addressing common challenges such as insurgency, terrorism, and transnational crimes. The porous border between the two countries has been a source of concern, facilitating the movement of insurgents, arms, and illicit activities.
Both governments have engaged in intelligence-sharing, joint patrolling, and capacity-building measures to enhance border security and combat cross-border threats. However, challenges persist due to the rugged terrain, ethnic diversity, and internal conflicts in border regions.

Challenges and Concerns:
Despite the significant progress in bilateral relations, India and Myanmar face several challenges and concerns that impede the full realization of their potential partnership.
One major challenge is the Rohingya crisis, which has strained relations between Myanmar and the international community, including India. India’s response to the Rohingya refugee issue has been a delicate balance between humanitarian concerns and strategic considerations, given its geopolitical implications and domestic political sensitivities.
Another challenge is the presence of insurgent groups along the India-Myanmar border, which pose security threats to both countries. Achieving lasting peace and stability in the region requires concerted efforts from both governments, as well as engagement with ethnic minority groups and civil society organizations.
Infrastructure development and connectivity projects face obstacles such as bureaucratic red tape, funding constraints, and logistical challenges, hindering their timely implementation. Additionally, divergent economic priorities and regulatory barriers can hamper trade and investment flows between India and Myanmar.
Future Prospects:
Despite the challenges, the India-Myanmar relationship holds immense potential for further growth and cooperation in various fields. Both countries recognize the strategic importance of deepening their ties to promote regional stability, economic development, and people-centric initiatives.
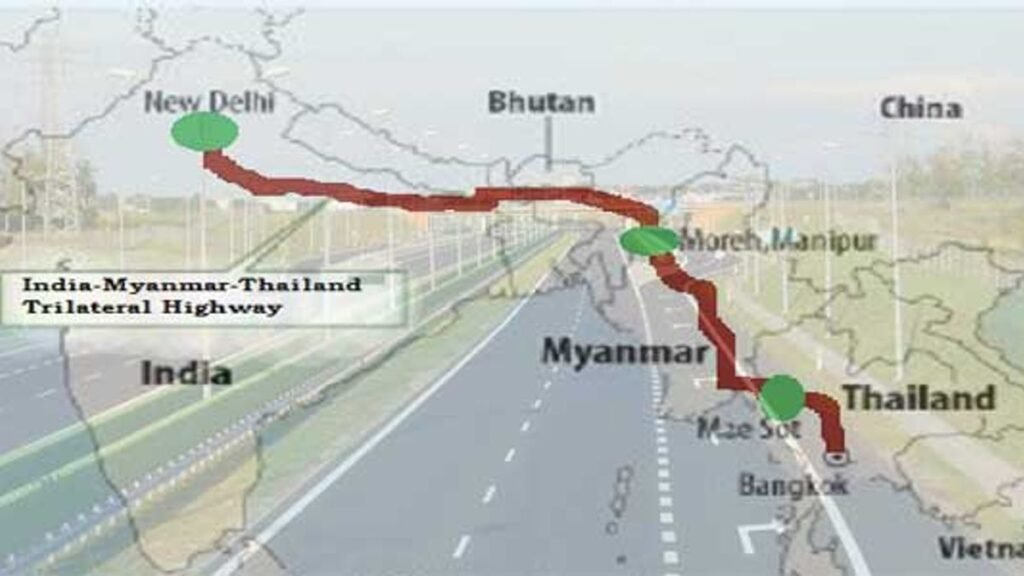
Efforts to strengthen connectivity, such as the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway and the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport Project, will bolster trade and investment flows, benefiting local communities and enhancing regional integration.
Cultural diplomacy and people-to-people exchanges will continue to foster mutual understanding and friendship between Indian and Myanmarese citizens, laying the foundation for stronger bilateral relations.
Addressing security challenges, including border management and counterterrorism cooperation, requires sustained engagement and collaboration between India and Myanmar’s security forces.
Humanitarian assistance and development cooperation, particularly in conflict-affected areas and border regions, can contribute to peace-building efforts and socioeconomic development.
As India and Myanmar navigate the complexities of regional geopolitics and internal challenges, a shared commitment to mutual respect, sovereignty, and inclusive development will be essential in shaping their enduring partnership.
Historical ties, strategic imperatives, and multifaceted cooperation across various sectors characterize the India-Myanmar relationship. While challenges persist, both countries remain committed to deepening their engagement and realizing the full potential of their bilateral partnership in the years to come.
