In the vast landscape of India’s financial sector, few innovations have been as transformative as the Unified Payments Interface (UPI). Launched in 2016 by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), UPI has revolutionized the way Indians transact, enabling seamless, instant, and secure peer-to-peer and peer-to-merchant payments. This comprehensive analysis delves into the origins, functionalities, impact, challenges, and prospects of UPI, highlighting its pivotal role in shaping India’s digital economy.
UPI payments are accepted in Singapore, Malaysia, UAE, France, Nepal, the UK, Mauritius, and Sri Lanka, to name a few. India is making significant strides in expanding the network of its digital payment systems like RuPay, and UPI (Unified Payments Interface), etc. Globally.
Origins and Evolution
The genesis of UPI can be traced back to the vision of fostering financial inclusion and digital empowerment in India. As traditional banking methods grappled with inefficiencies and limited outreach, the need for a unified and interoperable payment system became evident. In response, the NPCI conceptualized UPI as a revolutionary platform that would transcend barriers of geography, technology, and financial literacy.
Formally launched in April 2016, UPI was built upon the Immediate Payment Service (IMPS) infrastructure, leveraging the ubiquity of smartphones and the burgeoning internet penetration in India. Its architecture was designed to enable real-time fund transfers between bank accounts, bypassing the complexities associated with traditional payment methods such as NEFT and RTGS.
Functionalaties and Features
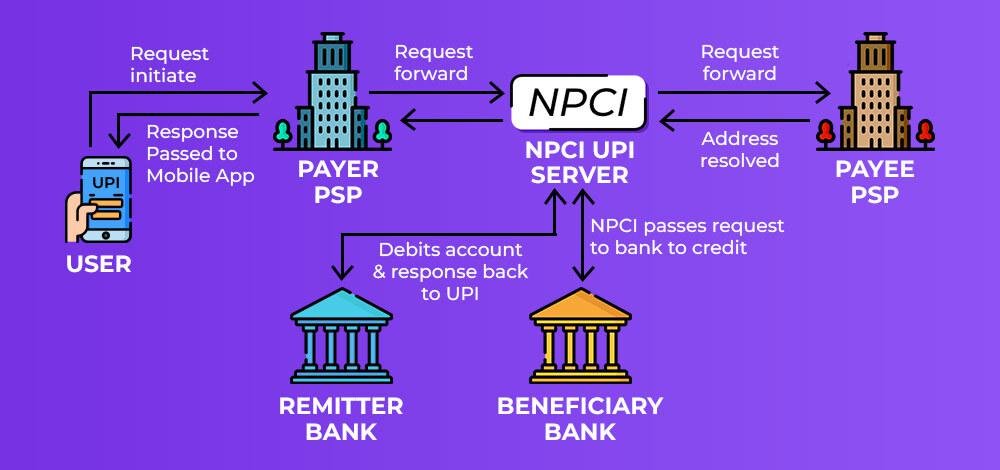
At its core, UPI operates as a layer atop existing banking infrastructure, facilitating seamless transactions through mobile applications. Users can register their bank accounts with any UPI-enabled app and create a unique Virtual Payment Address (VPA), eliminating the need to disclose sensitive information like account numbers and IFSC codes. Key functionalities of UPI include:
- Instant Transfers: UPI enables instantaneous transfer of funds 24/7, including weekends and holidays, fostering financial inclusivity and convenience.
- QR Code Payments: QR code technology integrated into UPI allows for swift and contactless payments at merchant outlets, driving adoption among businesses and consumers alike.
- Bill Payments and Recharges: UPI platforms offer a wide array of utility bill payment and mobile recharge services, consolidating diverse financial transactions within a unified interface.
- Request Money: Users can send payment requests directly through UPI apps, streamlining transactional workflows and enhancing user experience.
- UPI Mandates: The introduction of UPI mandates facilitates recurring payments such as EMIs, subscription services, and utility bill payments, enhancing automation and reducing friction in financial transactions.

Impact and Adoption of UPI
Since its inception, UPI has witnessed exponential growth, catalyzing a digital payments revolution across India. The following factors have contributed to its widespread adoption and profound impact:
- Inclusive Access: UPI transcends geographical barriers, enabling users from urban centers to remote villages to participate in the digital economy with minimal infrastructural requirements.
- Cost-effectiveness: With negligible transaction fees compared to traditional payment methods, UPI incentivizes merchants and consumers to embrace digital transactions, fostering financial efficiency and transparency.
- Ecosystem Integration: UPI has been seamlessly integrated into a myriad of applications and services, ranging from e-commerce platforms and ride-hailing apps to government initiatives such as BHIM (Bharat Interface for Money), amplifying its reach and utility.
- Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs): UPI empowers MSMEs by offering a hassle-free and cost-effective payment solution, enabling them to transact digitally and access a wider customer base.
- Financial Inclusion: UPI plays a pivotal role in advancing the government’s agenda of financial inclusion, and empowering marginalized communities and underserved populations with access to formal banking services.
Challenges and Regulatory Considerations
Despite its remarkable success, UPI faces several challenges and regulatory considerations that warrant attention:
- Security Concerns: As digital transactions surge, ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and fraud detection mechanisms is imperative to safeguard user data and trust in the ecosystem.
- Interoperability: While UPI promotes interoperability among banks and payment service providers, disparities in technological standards and operational procedures pose interoperability challenges that require harmonization.
- Privacy and Data Protection: With the proliferation of digital transactions, maintaining user privacy and adhering to data protection regulations emerge as critical imperatives for UPI stakeholders.
- Infrastructure Scalability: The exponential growth of UPI transactions necessitates continuous infrastructure scalability and resilience to support burgeoning transaction volumes without compromising service quality.
- Regulatory Framework: Evolving regulatory frameworks must strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring consumer protection, promoting a conducive environment for UPI’s sustainable growth.
Future Prospects and Innovation
Looking ahead, UPI is poised to play an even more transformative role in India’s digital economy, driven by ongoing innovations and strategic initiatives:
- International Expansion: Exploring opportunities for international expansion and interoperability with global payment systems can enhance UPI’s relevance on the global stage and facilitate cross-border transactions.
- Blockchain Integration: Leveraging blockchain technology can further enhance the security, transparency, and efficiency of UPI transactions, mitigating risks associated with centralized systems.
- AI and Machine Learning: Integrating AI and machine learning algorithms can bolster fraud detection, risk management, and personalized user experiences, enhancing the efficacy and resilience of UPI platforms.
- Smart Contract Integration: Incorporating smart contracts into UPI transactions can automate complex financial agreements, enabling frictionless execution and settlement of contractual obligations.
- Biometric Authentication: Embracing biometric authentication mechanisms such as fingerprint and facial recognition can bolster UPI security and streamline user authentication processes, enhancing convenience and trust.
The Unified Payments Interface stands as a testament to India’s prowess in fostering digital innovation and financial inclusion. By democratizing access to digital payments, UPI has catalyzed a paradigm shift in India’s financial landscape, empowering millions to participate in the digital economy. As UPI continues to evolve and expand its footprint, stakeholders must collaborate proactively to address challenges, harness emerging technologies, and unlock new avenues for growth, ensuring that UPI remains a cornerstone of India’s journey towards a cashless future.
