India and Nepal share a complex relationship that is deeply rooted in history, geography, culture, and politics. Situated in South Asia, these two nations have a long-standing association, characterized by both cooperation and periodic tensions. The Indo-Nepal relationship is multifaceted, encompassing economic ties, cultural exchanges, and political interactions. However, it is also marked by various disputes, particularly regarding territorial issues, water resources, and diplomatic matters. To understand the dynamics of the India-Nepal relationship, it is essential to delve into its historical background, examine the key areas of cooperation and contention, and explore potential avenues for resolving existing disputes.
Historical Background:
The history of India-Nepal relations dates back centuries, with both countries sharing deep cultural and religious ties. Nepal, with its rich Hindu and Buddhist heritage, has often been regarded as a spiritual and cultural counterpart to India. The close connection between the two nations was further strengthened by extensive trade and migration across their open borders.
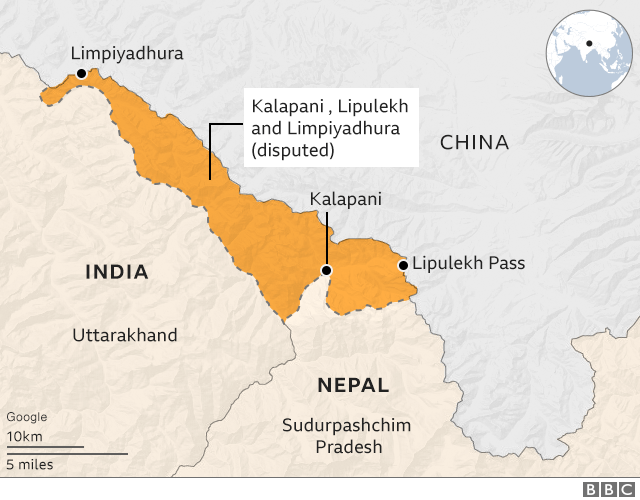
The Treaty of Sugauli in 1815-1816, which followed the Anglo-Nepalese War, formalized the relationship between British India and the Kingdom of Nepal. This treaty delineated the boundary between British India and Nepal, establishing a framework for bilateral relations. However, it also created some ambiguities and disputes regarding territorial demarcations, particularly in the border regions of Kalapani, Susta, and Limpiyadhura.
Key Areas of Cooperation:
Despite occasional tensions, India and Nepal have maintained robust cooperation in various domains:
- Trade and Economy: India is Nepal’s largest trading partner, and bilateral trade between the two countries encompasses a wide range of goods and services. The Treaty of Trade and Transit allows Nepal access to Indian ports for trade, contributing significantly to its economy.
- Security Cooperation: Both countries cooperate closely on security issues, including intelligence sharing and joint efforts to combat cross-border terrorism and insurgency.
- Cultural and People-to-People Contacts: Cultural exchanges between India and Nepal are vibrant, owing to their shared heritage and religious traditions. Thousands of Nepalese citizens travel to India for education, employment, and pilgrimage purposes, fostering people-to-people contacts.
- Development Assistance: India provides significant development assistance to Nepal, including infrastructure projects, educational initiatives, and capacity-building programs. This assistance aims to support Nepal’s socio-economic development and strengthen bilateral ties.
Disputes and Contentions:
Despite the historical and cultural affinity, India-Nepal relations have been strained by various disputes:
- Territorial Disputes: The Kalapani-Limpiyadhura-Lipulekh area in the Himalayas has been a longstanding bone of contention between India and Nepal. Nepal claims sovereignty over this region, which India currently administers. The dispute escalated in 2020 when India inaugurated a new road connecting the region to the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, triggering protests from Nepal.
- Water Resources: Nepal is a water-rich country, and its rivers are crucial for both nations. Disputes have arisen over the construction of dams and hydroelectric projects on rivers that flow from Nepal into India. Issues of water sharing, flood management, and environmental concerns have strained bilateral relations at times.
- Diplomatic Frictions: Periodic diplomatic tensions have surfaced between India and Nepal, often stemming from political developments within Nepal. Changes in Nepal’s domestic politics, including shifts in power dynamics and constitutional amendments, have sometimes led to diplomatic standoffs and public disagreements between the two countries.
- Trade Imbalances: Despite being Nepal’s largest trading partner, India’s dominance in Nepal’s market has raised concerns about trade imbalances and unequal economic relations. Nepal has sought to diversify its trade partners and reduce its dependence on India to safeguard its economic interests.
Recent Developments and Future Prospects:
In recent years, India-Nepal relations have witnessed both challenges and opportunities. The border dispute over the Kalapani-Limpiyadhura-Lipulekh region reached a boiling point in 2020, leading to heightened tensions and anti-India sentiments in Nepal. However, subsequent diplomatic engagements and high-level visits have aimed to defuse tensions and explore avenues for resolving outstanding issues.
Efforts to enhance connectivity and economic cooperation have also been underway, with initiatives such as the India-Nepal Integrated Check Post at Birgunj and the development of cross-border infrastructure projects. Additionally, cultural exchanges and people-to-people contacts continue to foster goodwill and understanding between the two nations.
Looking ahead, the India-Nepal relationship holds immense potential for cooperation and collaboration across various sectors. Both countries have a shared interest in promoting regional stability, economic development, and cultural exchange. Resolving longstanding disputes, such as the territorial issue and water resource management, will be crucial for building trust and strengthening bilateral ties.
Conclusion:
A complex interplay of historical bonds, geopolitical considerations, and contemporary challenges characterizes the India-Nepal relationship. While cooperation in trade, security, and culture forms the bedrock of their ties, disputes over territorial, water, and diplomatic matters have periodically strained relations between the two nations. However, the shared aspirations for peace, prosperity, and mutual respect provide a solid foundation for overcoming differences and charting a path toward a more robust and enduring partnership. By addressing existing disputes through dialogue, trust-building measures, and constructive engagement, India and Nepal can unlock the full potential of their relationship and contribute to the socio-economic development and stability of the South Asian region.
