General elections will be held in India from 19 April 2024 to 1 June 2024 to elect the 543 members of the 18th Lok Sabha. The elections will be held in seven phases and the results will be announced on 4 June 2024. Elections take place every 5 years to elect 543 members for the Lok Sabha (Lower house).
India is a constitutional democracy with a parliamentary
system of government, and at the heart of the system lies a
commitment to hold regular, free, and fair elections. These
elections determine the composition of the government, the
membership of the two Houses of Parliament, the State and
Union Territory Legislative Assemblies, and the Presidency and
Vice-Presidency.
Conduct of General Elections in India for
electing a new House of the People (Lower House of Indian
Parliament), involves management of the largest event in the
world. The electorate exceeds 605 million, voting in nearly
800,000 polling stations, spread across widely varying
geographic and climatic zones. Polling stations are located in
the snow-clad mountains in the Himalayas, the deserts of the
Rajasthan, and in sparsely populated islands in the Indian
Ocean.
The Election Commission is the federal body of India which is enacted under the provisions of the Constitution, responsible for monitoring and administering all the electoral processes of India. This body is responsible for ensuring elections are free and fair, without any bias.
Election ensures the conduct of members pre-elections, during elections, and post-elections are as per the statutory legislation.
The Election Commission handles all election-related disputes. The Supreme Court of India has held that where the enacted laws are silent or make insufficient provisions to deal with a given situation in the conduct of elections, the Election Commission has the residuary powers under the Constitution to act as appropriate.
Types of elections in India
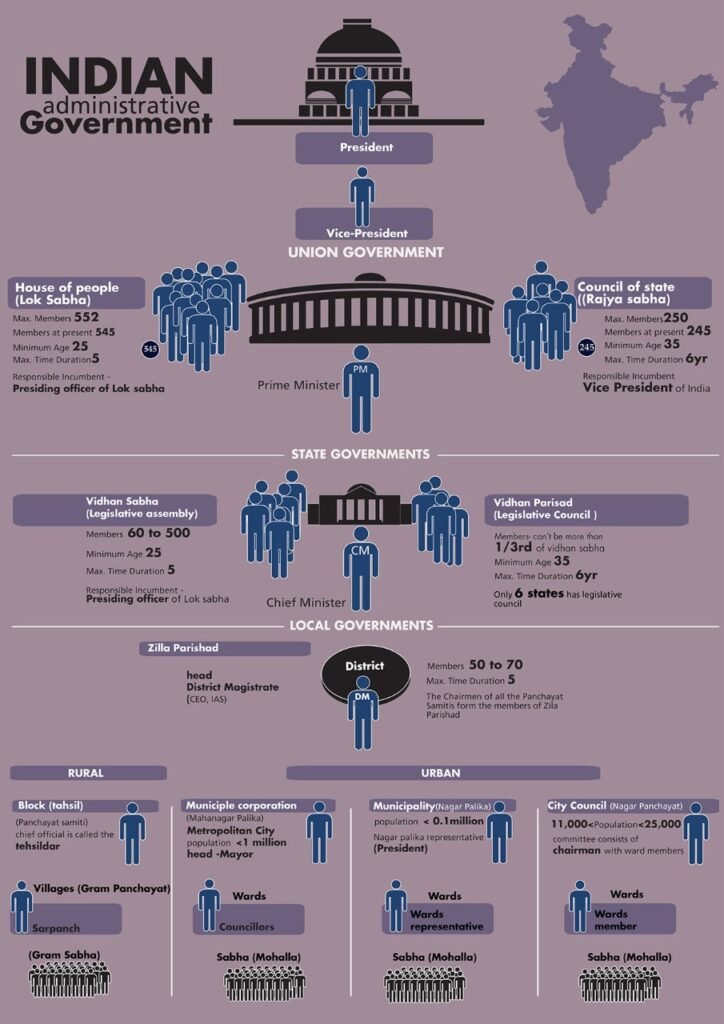
Parliament General Election (Lok Sabha)
The citizens aged 18 and above in the country elect the members of the Lok Sabha through direct voting. Each state is divided into territorial constituencies for elections. One member of Lok Sabha is elected from each constituency.
A candidate who is elected serves for five years. They are known as Members of Parliament. A total of 543 Lok Sabha members are chosen. Unless dissolved, the Lok Sabha continues to function for five years from the date of its first meeting.
Rajya Sabha Elections
Rajya Sabha members are elected indirectly by the people,
that is, by the MLAs.
Members of a state’s Legislative Assembly vote in the Rajya Sabha elections in
proportional representation with the single transferable vote (STV) system.
Each MLA’s vote is counted only once.
To win a Rajya Sabha seat, a candidate should get the required number of votes.
That number is found using the below formula. Required vote = Total
number of votes / (Number of Rajya Sabha seats + 1 ) + 1.5
State Assembly Election (Vidhan Sabha)
Assembly election is the election for the state legislative assembly. Each state is divided into territorial constituencies for elections. One member of the legislative assembly is elected from each constituency through direct voting. The elected members are called MLAs. The leader of the winning party becomes the chief minister of that state.
The maximum number of members of the legislative assembly is 500, and the minimum strength is 60. A candidate who gets elected holds their seat for five years. Currently, Himachal Pradesh and Gujarat are going to vote for State Assembly Election
Zila Panchayat / Autonomous District Council Election
Zila Parishad is the third tier of the Panchayati Raj system which administrates at the District level. The Zilla Parishad is a link between the State government and the Gram Panchayats. It is headed by a President who is elected directly from among the elected members of Zila panchayats of various districts. Each member of Zila Panchayat in different districts is elected directly by the citizens aged 18 and above. Each District (Zila) is divided into Gram Panchayats which are headed by a Pradhan Mukhiya or Sarpanch elected directly by the citizens of that village. Currently, Haryana is under polls for panchayat elections.
District Council for each autonomous district consisting of not more than thirty members, of whom not more than four persons shall be nominated by the Governor, and the rest shall be elected based on adult suffrage.

Municipal Election
Municipal Corporation Elections (India) are conducted to elect municipal councilors and ward representatives for Municipal Corporations in urban regions. The town is divided into wards according to its population, and representatives are elected from each ward. The members elect a president among themselves to preside over and conduct meetings. The Councillors or Ward Members are chosen by direct election from electoral wards in the Nagar Panchayats. Delhi will go under polls for municipal elections in December.
By-Election
A by-election or by-poll is an election used to fill an office that has become vacant between general elections. The seat could become vacant due to reasons like if a member of Parliament resigns, dies, switches parties, or if the candidate wins from both constituencies, they have to vacate one of the seats. A by-election is only open to voters of that particular constituency only who directly vote to elect the new member. Recently, Adampur, Munugode, Dhamnagar, Gopalganj, Mokama, Andheri West, and Gola Gokranath concluded their by-polls.
