Saudi Arabia and Qatar are two influential nations in the Middle East, sharing both commonalities and differences in their histories, ideologies, and geopolitical ambitions. Despite being neighbors and members of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), their relationship has been characterized by periods of cooperation, rivalry, and outright conflict. Understanding the dynamics between these two nations requires examining their historical background, regional ambitions, economic interests, and ideological differences.
Historical Background
The relationship between Saudi Arabia and Qatar dates back centuries, characterized by tribal affiliations, trade networks, and religious ties. Both nations share a common heritage rooted in Islam and Arab culture, but their paths diverged significantly in modern times.
During the early 20th century, both territories were under the control of the Ottoman Empire until the emergence of the modern Saudi and Qatari states. Saudi Arabia, founded in 1932 by Abdulaziz Ibn Saud, sought to consolidate power over the Arabian Peninsula, while Qatar, under the rule of the Al Thani dynasty, maintained its autonomy as a British protectorate until gaining independence in 1971.
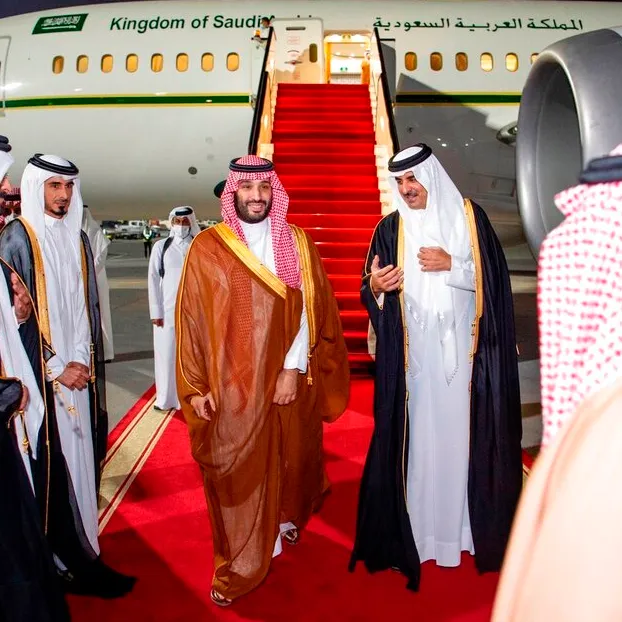

Political Relations
The political relations between Saudi Arabia and Qatar have oscillated between cooperation and tension, influenced by regional power struggles, ideological differences, and competition for leadership within the Arab world. The divergent foreign policies pursued by Riyadh and Doha have often led to confrontations, particularly in recent years.
One of the major sources of contention is Qatar’s independent foreign policy, which often diverges from the Gulf consensus led by Saudi Arabia. Qatar’s support for Islamist movements such as the Muslim Brotherhood and its relatively pragmatic approach towards Iran have irked Saudi leaders, who view these actions as undermining regional stability and Saudi Arabia’s leadership role in the Arab world.
Economic Interests
Economically, both Saudi Arabia and Qatar are major players in the global energy market due to their vast oil and gas reserves. While Saudi Arabia has historically been the dominant player within OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries), Qatar’s emergence as the world’s leading exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG) has challenged Saudi Arabia’s hegemony in the energy sector.

Despite their economic rivalry, both nations recognize the importance of cooperation in maintaining stability in the energy markets and have occasionally worked together within OPEC and other international forums to stabilize oil prices and defend their mutual interests.
Regional Conflicts
The rivalry between Saudi Arabia and Qatar has played out prominently in regional conflicts across the Middle East, particularly in the aftermath of the Arab Spring. Qatar’s support for Islamist groups and its involvement in the revolutions in Libya and Syria drew the ire of Saudi Arabia, which viewed these actions as destabilizing and contrary to its interests.
The most significant rupture in Saudi-Qatari relations occurred in 2017 when Saudi Arabia, along with its allies in the GCC, imposed a blockade on Qatar, accusing it of supporting terrorism and cozying up to Iran. The blockade, which included diplomatic isolation, economic sanctions, and restrictions on Qatar’s access to airspace and shipping lanes, pushed Qatar closer to Iran and Turkey, further exacerbating tensions within the GCC.
Mediation Efforts
Efforts to mediate the Saudi-Qatari dispute have been made by various actors, including Kuwait and the United States, but a lasting resolution has remained elusive. While there have been occasional signs of rapprochement between the two nations, such as Qatar’s participation in the GCC summit in 2021, deep-seated grievances and mistrust continue to hinder meaningful progress towards reconciliation.
Impact on the Region
The rift between Saudi Arabia and Qatar has had significant implications for regional dynamics, reshaping alliances, and exacerbating existing conflicts. The emergence of competing blocs led by Saudi Arabia and Qatar has polarized the Gulf region, complicating efforts to address common challenges such as extremism, sectarianism, and Iranian influence.
Moreover, the Saudi-Qatari rivalry has contributed to the fragmentation of the Arab world, weakening the collective ability of Arab states to confront external threats and pursue shared interests. The absence of Gulf unity has also emboldened regional actors such as Iran and Turkey, who have sought to exploit divisions within the GCC to advance their agendas.
A complex interplay of historical, political, economic, and ideological factors characterizes the relationship between Saudi Arabia and Qatar. Despite sharing common cultural and religious ties, the two nations have often found themselves at odds due to competing interests and divergent foreign policies.
The ongoing rift between Saudi Arabia and Qatar has far-reaching implications for the Gulf region and the broader Middle East, exacerbating existing conflicts, undermining regional stability, and weakening the collective ability of Arab states to address common challenges. While occasional attempts at reconciliation have been made, the deep-seated grievances and mistrust between Riyadh and Doha continue to hinder meaningful progress toward resolving their differences and restoring Gulf unity.
