Iran and Iraq share a complex and multifaceted relationship that spans centuries of history, encompassing cultural, religious, economic, and geopolitical dimensions. This relationship has been marked by periods of cooperation, rivalry, conflict, and mutual interests, shaped by regional dynamics, international politics, and domestic factors within each country. It’s essential to delve into their historical background, examine key events and developments, analyze the current state of affairs, and explore prospects to understand the intricacies of Iran-Iraq relations.
Historical Background:
Ancient Times:
- Pre-Islamic Era: The territories of present-day Iran and Iraq were part of ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia and Persia. These lands witnessed the rise and fall of empires like the Babylonians, Assyrians, Medes, and Achaemenids, which contributed to the cultural and historical ties between the two regions.
Islamic Period:
- Arab Conquest: In the 7th century, Arab Muslims conquered both Iran and Iraq, bringing Islam to the region. While Iraq became the center of the Islamic caliphate under the Umayyad and Abbasid dynasties, Iran experienced its own cultural and political evolution under various Persian dynasties.
- Persian Influence: Despite Arab rule, Persian culture, language, and traditions persisted in Iran, contributing to a distinct Persian identity within the Islamic world.
Ottoman and Safavid Empires:
- Ottoman-Iranian Rivalry: During the Ottoman and Safavid empires’ rule (16th-18th centuries), Iran and Iraq were often battlegrounds for territorial disputes and religious conflicts between Sunni Ottoman Turks and Shia Safavids. The borderlands between the two empires were frequently contested.

Modern Era:
- Colonial Interference: In the 19th and early 20th centuries, both Iran and Iraq experienced European colonial influence, with Britain asserting control over Iraq and exerting significant influence in Iran.
- Pahlavi Era: Reza Shah Pahlavi’s rise to power in Iran and his efforts to modernize the country shifted Iran’s focus toward its domestic affairs, somewhat diminishing its engagement with Iraq.
Twentieth Century:
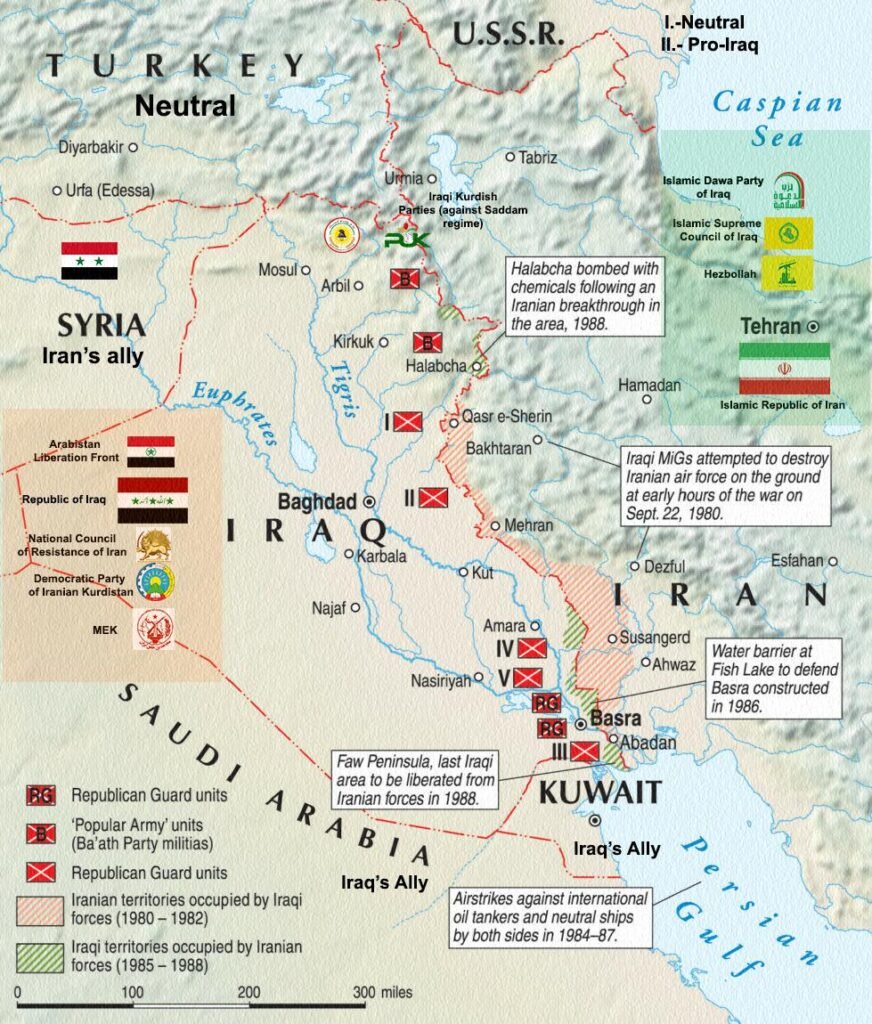
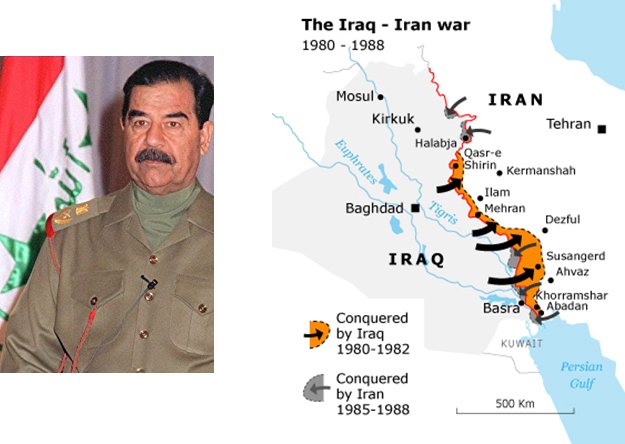
Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988):
- Causes: The Iran-Iraq War was fueled by territorial disputes, ideological differences, and ambitions for regional dominance. Iraqi leader Saddam Hussein’s desire to assert Iraqi hegemony and weaken Iran’s revolutionary zeal played a crucial role.
- Impact: The war resulted in immense human and economic costs for both countries. Despite international support for Iraq, neither side achieved a decisive victory, and the conflict ended in a stalemate with millions dead or injured and significant infrastructure damage.
Post-War Dynamics:
- Strained Relations: The aftermath of the war left deep scars on Iran-Iraq relations. Suspicion, animosity, and mistrust persisted, exacerbated by Iraq’s use of chemical weapons against Iranian forces and civilians.
- Geopolitical Shifts: The Gulf War of 1990-1991 and the subsequent establishment of a no-fly zone in northern Iraq and a Shia uprising in the south further reshaped regional dynamics, with Iran cautiously observing the developments.
Twenty-First Century:
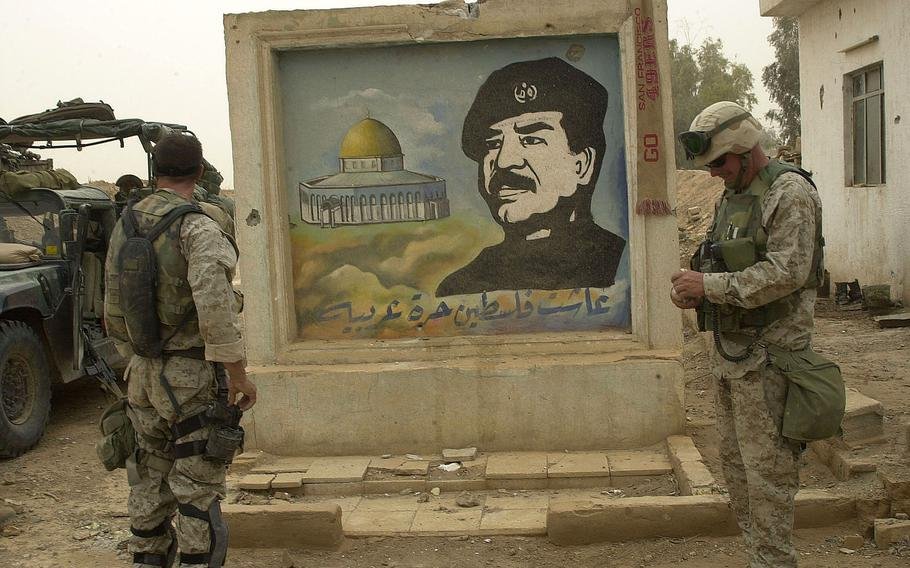
Post-Saddam Iraq:
- US Invasion: The overthrow of Saddam Hussein’s regime in 2003 by a US-led coalition dramatically altered the geopolitical landscape of the region. The invasion removed a longstanding adversary of Iran but also introduced significant instability and sectarian tensions in Iraq.
- Shia Dominance: The rise of a Shia-dominated government in Baghdad following the US occupation shifted the balance of power in Iraq, aligning its interests more closely with Iran’s, given Iran’s predominantly Shia population and the shared religious ties between the two countries.
Economic Cooperation:
- Trade and Energy: Iran and Iraq possess vast energy resources, and both countries have sought to leverage their oil and gas reserves for economic development. Despite occasional tensions, they have engaged in trade and energy cooperation, with Iran supplying electricity and natural gas to Iraq.
Cultural and Religious Ties:
- Shia Islam: The majority of Iraq’s population adheres to Shia Islam, the same branch as Iran’s dominant religion. This shared religious affinity has fostered cultural and religious exchanges, pilgrimage tourism, and educational ties between the two countries.
- Cultural Exchanges: Despite political differences, Iranian and Iraqi cultural ties remain strong, with shared traditions, language, literature, and historical heritage.

Geopolitical Considerations:
- Regional Power Dynamics: Both Iran and Iraq aspire to assert influence in the Middle East, albeit through different means and alliances. Iran’s support for Shia militias in Iraq and its involvement in regional conflicts have raised concerns among Iraq’s Sunni and Kurdish communities and drawn criticism from neighboring Sunni-majority states.
- US-Iran Rivalry: The ongoing rivalry between the United States and Iran has had reverberations in Iraq, with Iraq often caught in the middle of competing interests. While Iran seeks to expand its influence in Iraq, the US aims to maintain its strategic presence and counter Iranian influence.
Security Cooperation:
- Counterterrorism: Both Iran and Iraq have faced significant security challenges, including terrorism, insurgency, and sectarian violence. Despite their differences, they have cooperated, to some extent, in combating common threats posed by extremist groups like ISIS (Islamic State of Iraq and Syria).
- Border Security: Managing the long and porous border between Iran and Iraq presents security challenges for both countries, including smuggling, illegal migration, and the movement of armed groups.
Current Dynamics:
Political Relations:
- Government Interactions: Iran and Iraq maintain diplomatic relations, with frequent high-level exchanges between their respective governments. However, political ties are often influenced by domestic considerations, regional developments, and international pressures.
- Influence Operations: Iran has sought to exert influence in Iraq through various means, including support for Shia political parties, militias, and religious institutions. This influence has raised concerns among Iraq’s Sunni and Kurdish communities and triggered accusations of Iranian interference in Iraqi affairs.
Economic Interdependence:
- Trade and Investment: Despite sporadic tensions, economic ties between Iran and Iraq have grown in recent years, with bilateral trade, investment, and energy cooperation benefiting both countries. Iran remains a significant trading partner for Iraq, particularly in sectors such as energy, construction, and agriculture.
- Cross-Border Infrastructure: Projects such as the Shalamcheh-Basra railway and the construction of border crossings aim to enhance connectivity and facilitate trade and people-to-people exchanges between Iran and Iraq.
Security Challenges:
- Militancy and Insurgency: Both Iran and Iraq grapple with the threat of militancy and insurgency, fueled by domestic grievances, sectarian tensions, and external influences. While Iran has supported Shia militias in Iraq to counter Sunni extremist groups, Iraq seeks to assert its sovereignty and maintain security without undue foreign interference.
- US Presence: The presence of US military forces in Iraq remains a contentious issue, with Iran viewing it as a threat to its regional interests and Iraq torn between balancing its relations with Iran and its security partnership with the United States.
Regional Developments:
- Saudi-Iran Rivalry: The rivalry between Iran and Saudi Arabia for regional influence has implications for Iraq’s stability and security. Iraq seeks to balance its relations with both Iran and Saudi Arabia to avoid being drawn into broader regional conflicts.
- Syria Conflict: Iran’s involvement in the Syrian civil war, in support of the

Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites